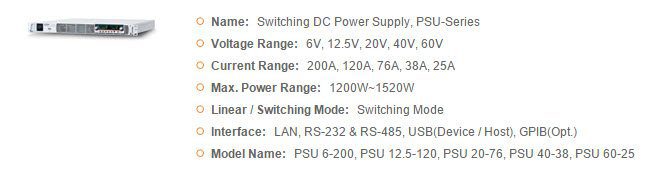
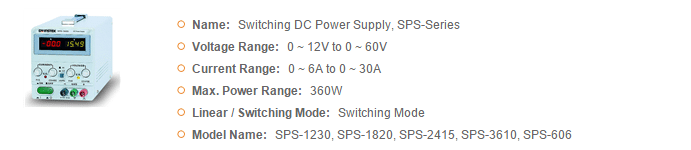
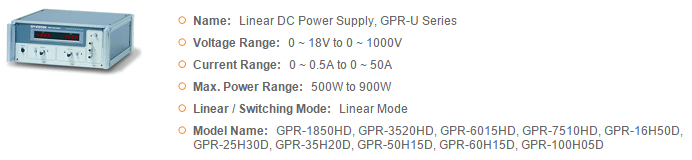
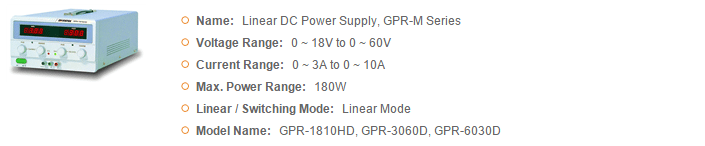
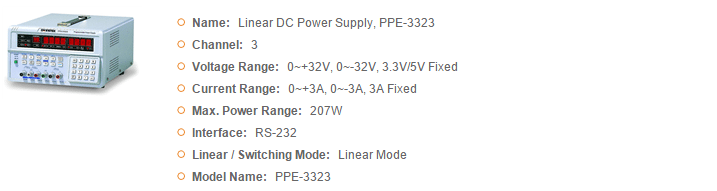
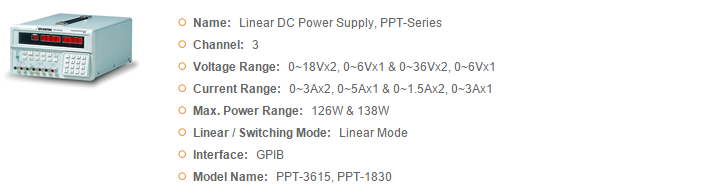
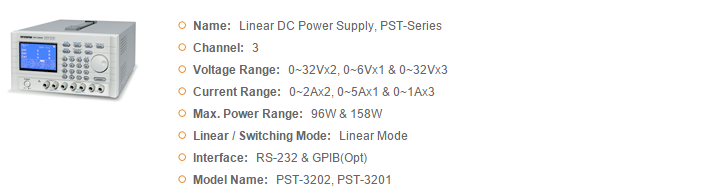
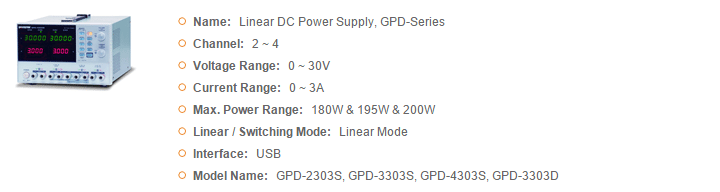
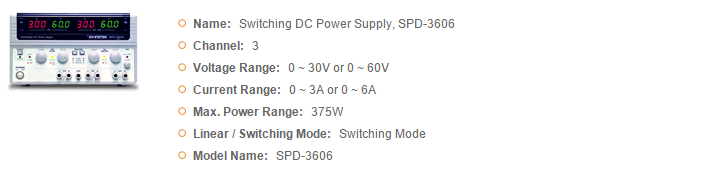
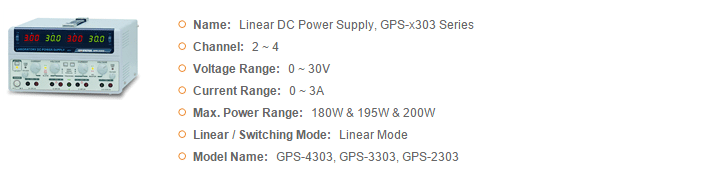
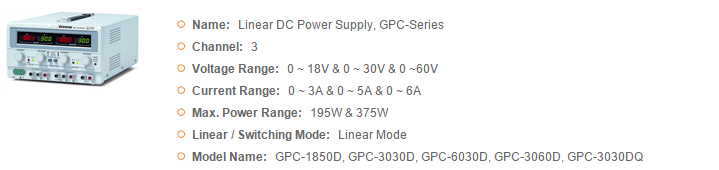
GWInstek Power Supplies
GSAS microsystems is an authorized distributor for GWInstek which offers diverse power supplies product lines to meet user’s demand for a variety of applications. Based on different needs, the product lines can be divided into several categories including DC Power Supply, AC Power Source, and DC Electronic Load. For DC Power Supply, the products can be briefly categorized by the following types, Linear, Switching, Programmable or Non-programmable, Single or Multiple Outputs, High Precision or Affordable Price, Dual Range and Wide Combinations of Voltage and Current, which can be selected to meet the application requirements.
Understanding AC and DC Power Supplies
There are two primary types of electrical power supplies: AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current).
What is AC Power Supply?
AC power supply delivers electrical energy where the current periodically changes direction. This means that both the voltage and the current regularly reverse. This type of power supply is widely used in homes and commercial buildings to power various electrical devices. Additionally, AC power is the standard for the distribution of electricity over long distances. It is typically generated by electric power stations utilizing rotating machines such as turbines or generators.
What is DC Power Supply?
On the other hand, a DC power supply provides electrical energy that flows in a single direction, ensuring that both the voltage and the current remain constant. DC power is essential for many electronic devices and systems, as well as for transportation technologies, including electric cars, buses, and trains. Sources of DC power include batteries, solar panels, and specialized DC power supplies.
Key Differences Between AC and DC Power
- Direction and Frequency: AC power changes direction periodically, while DC power flows consistently in one direction.
- Usage: AC power is predominantly used for transmitting electricity and powering buildings. In contrast, DC power is preferred for electronic devices and various transportation systems.
Practical Applications
- AC Power: Commonly found in residential and commercial settings for powering appliances, lighting, and HVAC systems.
- DC Power: Utilized in battery-operated devices, solar power systems, and electric vehicles.
By understanding the fundamental differences and applications of AC and DC power supplies, you can better appreciate their roles in modern technology and everyday life.